Taxation of Tokumei Kumiai Investment
You may have an investment in Japanese silent partnership so-called Tokumei Kumiai (TK). TK is one of the standard structure for investment in Japanese real estate or solar panels. Taxation would differ depending on whether TK investor is Japanese tax resident or non-resident. We summarize Japanese taxation when an investor has TK investment.
Tokumei Kumiai (TK) structure
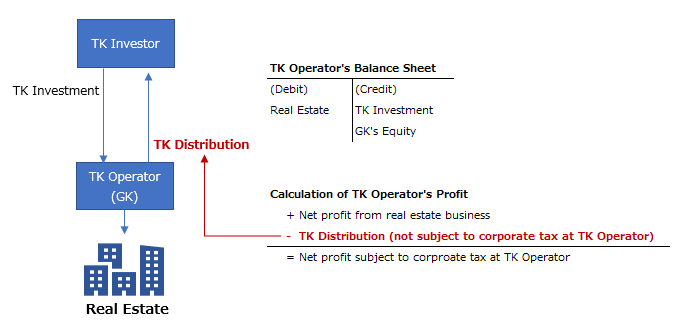
Tokumei Kumiai is an agreement stipulated under Article 535 of Japanese Commercial Code, that is, investor (TK Investor) promises to contribute to an operator of business (TK Operator), and the operator promises to distribute profits arising from its business (TK Distribution) to the investor.
The crucial difference from a stock investment for Japanese tax purposes is that TK investor can receive a profit which is not subject to corporate taxation at TK Operator level.
When TK is used for investment in Japanese real estate or solar panels, Japanese Godo Kaisha (GK) is often established as TK Operator. The structure using TK and GK is sometimes known as “TK-GK Structure.”
Standard TK-GK Structure is illustrated as follows:
Where Japanese tax resident receives Tokumei Kumiai (TK) Distribution
TK Distribution to Japanese tax resident individual or corporation is subject to Japanese withholding tax at the rate of 20.42% (including sur-tax).
Also, where a resident individual receives the TK Distribution, he/she needs to report the distribution generally as “Other Income” by filing income tax return. Progressive tax rate up to approximately 56% (including surtax and local tax) is applied to the Other Income together with other categories of income such as salary income or rental income and so on.
In the case of a resident corporation, TK Distribution is subject to Japanese corporate tax at the investor level. The effective corporate tax rate is approximately 30% where the share capital of the corporation exceeds JPY 100 million.
Withholding tax is creditable against the annual individual or corporate tax calculated on the tax return.
Where non-resident receives Tokumei Kumiai (TK) Distribution
TK Distribution to non-resident is also subject to Japanese withholding tax at the rate of 20.42% (including sur-tax).
However, TK Distribution received by a non-resident individual is not subject to progressive taxation. Also, non-resident individual needs not file an income tax return for the distribution. Accordingly, withholding tax at 20.42% can be the final tax in case of the non-resident individual.
A non-resident corporation is also subject to the same rule as a non-resident individual. Therefore, withholding tax at 20.42% can also be the final tax for the non-resident corporation.
Generally speaking, tax treaties Japan conducts do not reduce or exempt the taxation of TK distribution to non-resident (although a few tax treaties still can exempt).
Please note we assume “non-resident” in this context does not have a permanent establishment in Japan.
————
This post is a summary based on the applicable tax laws and regulations of Japan effective as at the date hereof. Before making any decision or taking any action, you should consult with other professionals or us.

