Filing obligation of consumption tax return
Japanese consumption tax is equivalent to the Value Added Tax (VAT) or Goods and Service Tax (GST) in other countries. As well as VAT or GST, the Japanese consumption tax system is complex. In particular, the determination of filing obligation of consumption tax might be a bit confusing, although it is essential to operate a business in Japan.
This article summarises an overview of how to determine the filing obligation of the Japanese consumption tax return.
Taxable transactions and tax rate
In general, the following transactions (Taxable Transactions) are subject to the Japanese consumption tax.
- Transfer of goods located in Japan
- Lease of goods located in Japan
- Provision of service in Japan
The tax rate of consumption tax is currently 10%. Reduced rate of 8% may apply if the goods sold in Japan are certain foods or newspapers.
Export of goods or services are also treated as Taxable Transactions, but 0% consumption tax rate is generally applied (Export Transactions).
Also, financial transactions such as interest payments, etc., or certain other transactions stipulated under the Japanese consumption tax law are generally treated as a non-taxable.
Filing obligation of consumption tax return
Where a corporation recognizes Taxable Transactions as revenue, the corporation is generally obliged to file a consumption tax return and to pay the consumption tax calculated in the tax return within two months after the end of its fiscal year.
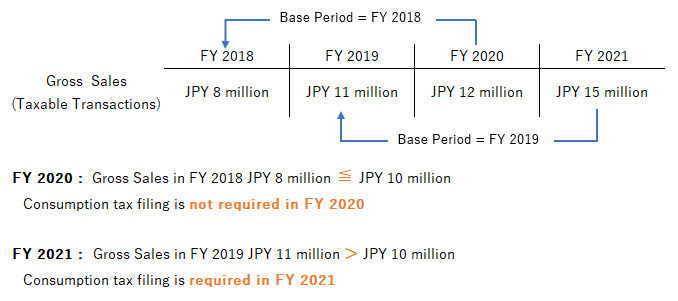
However, if the total of Taxable Transactions (including Export Transactions) in the “Base Period” (as explained below) is JPY 10 million or less, the filing obligation of consumption tax return should generally be exempt.
“Base Period” is a fiscal year two years before the current fiscal year in the case of a corporation whose fiscal year is set as twelve months.
For example, based on the following case, filing obligation in FY 2020 and FY 2021 should be determined as follows:
Major points to note
(1) Charge of consumption tax
Under the current consumption tax law at the date of this article, a corporation can charge a consumption tax on Taxable Transactions in its invoice, even if the corporation does not have to file the consumption tax return in the year.
In this case, consumption tax received from the customer (Output Consumption Tax) can also be a revenue of the corporation since the corporation does not have to pay the Output Consumption Tax to Japanese tax authorities in the year.
However, when the Japanese invoice system on consumption tax is introduced on or after October 1, 2023, the above tax treatment might be gradually restricted.
(2) Consumption tax to be paid by filing the tax return
As explained above, a corporation is required to file the consumption tax return if the total of Taxable Transactions (including Export Transactions) in the Base Period was more than JPY 10 million.
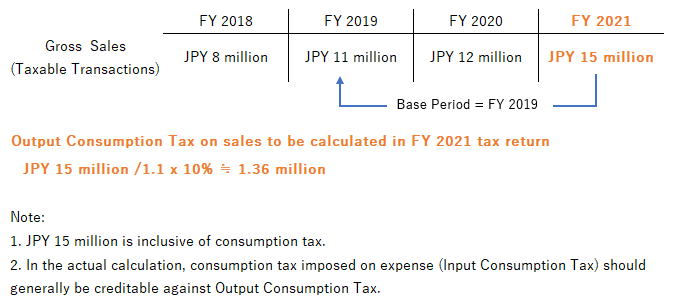
In this case, consumption tax to be paid by filing the tax return is not a consumption tax collected in the Base Period, but the current year.
Using the same example as above, consumption tax to be paid by filing the tax return in 2021 should be calculated based on Taxable Transactions to be recognized in 2021.
(3) Application to a newly established corporation without Base Period
In the case of a newly established corporation, the corporation does not generally have to file the consumption tax return in the first two fiscal years from its establishment since there should be no Base Period.
However, the above filing exemption rule for the newly established corporation should not be applied it the amount of share capital is JPY 10 million or more.
(4) Application to foreign corporations
The above rules on filing obligation of consumption tax also applied to foreign corporations, even if they do not have a Japan branch.
Therefore, a foreign corporation might need to file a consumption tax return if it recognizes Taxable Transactions exceeding JPY 10 million in a year and continues to recognize Taxable Transactions in other subsequent years.
Several exceptions to consumption tax filing exemption
As explained above, a corporation does not have to file the consumption tax return if the total of Taxable Transactions (including Export Transactions) in the Base Period is JPY 10 million or less.
However, there are several exceptions to the above general rule. For example, corporations need to file a consumption tax return if:
(1) the total of Taxable Transactions (including Export Transactions) in the first six months of immediately preceding fiscal year of the current fiscal year was more than JPY 10 million; and
(2) salary during the same six months was also more than JPY 10 million.
If you have any concerns about filing obligation of consumption tax return, please consult with your tax advisor or contact us.
————
This post is a summary based on the applicable tax laws and regulations of Japan effective as at the date hereof. Before making any decision or taking any action, you should consult with other professionals or us.

