Japanese withholding tax imposed on non-resident
If a non-resident receives some Japanese source income, such income might be subject to Japanese withholding tax even if the non-resident does not have a permanent establishment (PE) in Japan.
“Non-resident” in this article generally means a non-resident individual and a foreign corporation for Japanese tax purposes.
Income subject to Japanese withholding tax
Here are examples of Japan source income that non-residents are subject to Japanese withholding tax under the Japanese domestic tax law.
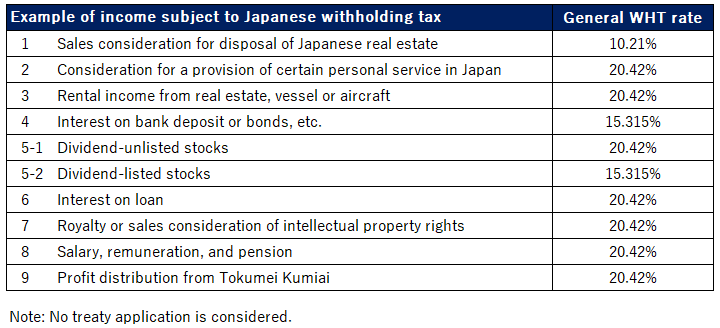
Please note this is not a comprehensive list. Other types of income might also be subject to Japanese withholding tax. Also, the withholding tax rates below include surtax.
1.Sales consideration for disposal of Japanese real estate
Where a seller of Japanese real estate is non-resident, a buyer has to withhold Japanese income tax from the sales consideration.
The withholding tax rate is 10.21% of sales consideration (not a capital gain).
In some cases, withholding tax obligation of the buyer might be exempt under the Japanese tax law.
2.Consideration for a provision of certain personal service in Japan
Where a non-resident conducts business providing certain personal service in Japan, consideration for such business should be subject to Japanese withholding tax at the rate of 20.42%.
Typical examples are talent agency business or professional service firm (e.g., lawyer or accountant). However, other types of businesses might also fall under this category since the scope of the personal services is broadly defined under the Japanese tax law.
3.Rental income from real estate, vessel or aircraft
Rental income from Japanese real estate, consideration of lending a vessel/aircraft to Japanese residents, etc. are generally subject to Japanese withholding tax at the rate of 20.42%.
In some cases, withholding tax might be exempt under the Japanese tax law.
4.Interest on bank deposit or bonds, etc.
Interest income on bank deposit or bonds, etc. which is treated as Japan source income for tax purposes are subject to withholding tax at the rate of 15.315%.
There are some exemptions. For instance, interest income on Japanese government bonds or certain corporate bonds which are treated as book-entry bonds can be exempt from withholding tax by applying necessary procedures.
Please note that withholding tax treatment for interest on a loan is separately stipulated under the Japanese tax law (see 6. below).
5.Dividend
Dividend paid by Japanese corporations or distribution of Japanese investment trust, etc. are subject to Japanese withholding tax.
General withholding tax rate is 20.42%. However, if it is paid by a listed corporation or publicly offered investment trust, the tax rate reduces to 15.315%.
6.Interest on loan
Interest on a loan provided to a person operating a business in Japan is subject to Japanese withholding tax at the rate of 20.42%.
Loan to a Japanese corporation by a foreign corporation based on a loan agreement is the typical case.
7.Royalty or sales consideration of intellectual property rights
Royalties or sales considerations of certain intellectual property rights received from a person operating a business in Japan should be subject to Japanese withholding tax at the rate of 20.42%.
The same taxation should apply to certain royalty for machinery, equipment, etc.
In practice, the scope of royalties subject to withholding tax might be argued.
8.Salary, remuneration, and pension
Salary or bonus to be treated as salary income for Japanese tax purposes is subject to withholding tax for the portion corresponding to the working period in Japan.
However, please note director’s remuneration paid by Japanese corporations to non-resident director should be entirely subject to the withholding tax. This tax treatment is applied even where he/she was not working in Japan at any time.
Some retirement allowance or pension income also fall under this category.
Applicable withholding tax rate is 20.42%.
Regarding retirement income, please also see the article below.
Related Post:
Japanese tax refund of retirement income
9.Profit distribution from Tokumei Kumiai
Profit distribution from Tokumei Kumiai is subject to Japanese withholding tax at the rate of 20.42%.
Please see the article below for detail.
Related Post:
Taxation of Tokumei Kumiai Investment
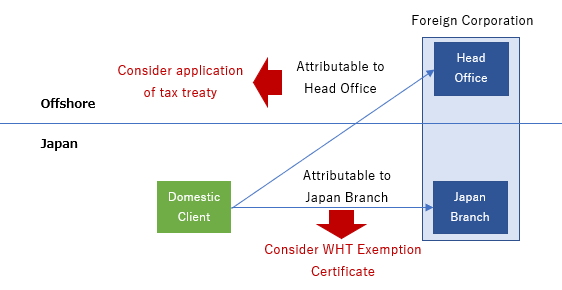
Where non-resident has PE in Japan
Same withholding tax rule should apply even where non-resident has PE in Japan (e.g., Japan branch of a foreign corporation).
However, if the PE of non-resident has so-called “withholding tax exemption certificate”(源泉免除証明書) issued by Japanese tax authorities, some of the withholding tax can be exempt.
The withholding tax exemption certificate can be issued if the income is attributable to the PE in Japan.
Application of tax treaty
Explanations above are based on Japanese domestic tax law.
Japanese withholding tax rate might be reduced or exempt if:
- there is a tax treaty between Japan and the country where the non-resident resides; and
- the income is not attributable to the PE in Japan.
However, not all withholding tax rate on Japan source income can be reduced or exempt. Also, to apply the tax treaty, non-resident has to file a specific application to Japanese tax authorities before receiving the income.
The application of withholding tax exemption certificate and tax treaty is briefly illustrated as below.
Filing requirement
In general, Japanese withholding tax can be the final tax for non-resident without PE in Japan (e.g., interest, dividend and royalty).
However, certain Japan source incomes require non-resident taxpayer without PE in Japan to file a tax return to Japanese tax authorities.
Some of Japan source income listed above (e.g., rental income from Japanese real estate) is subject to the tax filing requirement. However, in this case, the non-resident taxpayer can report taxable income by deducting related expenses from the Japan source income. Therefore, the non-resident taxpayer can generally claim a refund of withholding tax by filing the tax return.
Please also note there are certain Japan source incomes which are not subject to withholding tax, but the non-resident taxpayer has to file a tax return.
————
This post is a summary based on the applicable tax laws and regulations of Japan effective as at the date hereof. Before making any decision or taking any action, you should consult with other professionals or us.

